Animations are the things that make graphic objects active to display data/status/history etc. or receive some user input or commands.
Most of the animations have a code that defines a value or a condition (true/false) the animation use to determine its state. When the code associated with the animation changes, then the animation is updated.
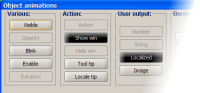 To add/edit animation of selected graphic object use the
To add/edit animation of selected graphic object use the  toolbar button or the Enter key to open the Object animation dialog which enable to add and edit the animation allowed for the selected graphic object.
toolbar button or the Enter key to open the Object animation dialog which enable to add and edit the animation allowed for the selected graphic object.
To quickly edit the tag used by the animations of an object see Editing graphic object tags.
Type of animations
A brief description for every type of animation that JSup provides. For more detail (where no animation specific page is available) use the specific animation dialog tooltip.
Various
- Visible: define when an object has to be visible and when to hidden (delayable).
- Opacity: define how opaque or transparent the object has to be (smoothable).
- Blink: define when and how the object has to blink.
- Enable: define when the object have to receive user inputs and when not (delayable).
- Rotation: define how/when the object has to rotate (smoothable).
Action
These animations are disabled when an Enable animation on the same object or a containing binder tells to disable them.
- Action: define a piece of code that will be executed when the user click over the object (or press the given shortcut, if any) (secureable).
- Show win: define which windows will be displayed when the user clicks over the object (or press the given shortcut, if any) (secureable).
- Hide win: define which windows will be hidden when the user clicks over the object (or press the given shortcut, if any) (secureable).
- Tooltip: a piece of code that return the
 tooltip string that will be displayed when the user points the animated object with the mouse cursor.
tooltip string that will be displayed when the user points the animated object with the mouse cursor.
- Locale tip: Define a default language tip and many localized version of that tip (for multi language application), the displayed tip will depend of the JSup current locale.
User input
Available for Java GUI objects only. These animations are disabled when an Enable animation on the same object or a containing binder tells to disable them.
- Number input: enable the user to enter a number in the Text field/Text area. Min/max can be specified, the format is the static string of the object (secureable). See JavaCode tag references.
- String input: enable the user to enter a string in the Text field/Text area. Max length can be specified (secureable). See JavaCode tag references.
- Custom input: a special animation for Text field/Text area that provides a custom output code, used to display the value, and a custom input parser code that processes the user input (secureable). See the standard JSup Trend window (the trend length field) for an example of this kind of animation.
- Boolean input: connects a Checkbox with a boolean tag value (see JavaCode tag references). When the user changes the checkbox selection state the value of the tag is changed, and when the tag is elsewhare changed the checkbox state is updated (secureable).
- List input: provides the content (the model
 ) of a list object (secureable). The destination tag (see JavaCode tag references) can receive/provide the selected index (0 based) or the selected value. The list content can be provided in three ways:
) of a list object (secureable). The destination tag (see JavaCode tag references) can receive/provide the selected index (0 based) or the selected value. The list content can be provided in three ways:
- Static: a text whose lines will be the list items.
- Tag array whose elements will be the list items.
- Java ListModel
 : a JavaCode returning an object that implements the ListModel
: a JavaCode returning an object that implements the ListModel  interface
interface  .
.
- Combobox input: provides the content (the model
 ) of a Combo box object (secureable). The destination tag (see JavaCode tag references) can receive/provide the selected index (0 based) or the selected value. The combo box can be editable so the user can both select or type the desired value. The combo box content can be provided in three ways:
) of a Combo box object (secureable). The destination tag (see JavaCode tag references) can receive/provide the selected index (0 based) or the selected value. The combo box can be editable so the user can both select or type the desired value. The combo box content can be provided in three ways:
- Static: a text whose lines will be the combo items.
- Tag array whose elements will be the combo items.
- Java ComboBoxModel
 : a JavaCode returning an object that implements the ComboBoxModel
: a JavaCode returning an object that implements the ComboBoxModel  interface
interface  .
.
- Tree combo: a piece of code that have to initialize a Tree Combo object by calling the setModel() or setRoot() methods. This animation can be used to provide the user the possibility to select an alarm group (with the getAlarmGroupTreeNodeProvider() utility function) or a security group (with the getSecurityGroupTreeNodeProvider() utility function). This is a secureable animation.
- Calendar combo enable the user to select, in Calendar combo, a date and to assign it to a long tag (as millisecond from midnight, 01 January 1970, as System.currentTimeMillis()
 in Java API
in Java API  ) or an object tag of Date
) or an object tag of Date  or Calendar
or Calendar  type (see JavaCode tag references). The output of the Calendar combo object can be formatted with standard (Short/Medium/Long/Full) localized format or with a custom format (see the java.text.SimpleDateFormat
type (see JavaCode tag references). The output of the Calendar combo object can be formatted with standard (Short/Medium/Long/Full) localized format or with a custom format (see the java.text.SimpleDateFormat  class documentation).
class documentation).
- Alarm display enable a table object to display real time alarms for the given alarm groups and with the selected column.
- Java TableModel a way to provide the content of JSup Table object. The JavaCode must return an object that implements the javax.swing.table.TableModel
 interface. The JavaCode have the access to the JTable
interface. The JavaCode have the access to the JTable  object that will display the table content via the table parameter. The column widths can also be provided by the animation, see the tooltip for the help.
object that will display the table content via the table parameter. The column widths can also be provided by the animation, see the tooltip for the help.
- Slider links the value of a numeric tag (see JavaCode tag references) to a slider object, so the user can set the value of the tag with the mouse. Min/max values can be constant or dynamic expressions; the same for the optional maj/min tick expression fields. (secureable)
- Spinner link the value of a numeric tag (see JavaCode tag references) to a spinner object, so the user can set the value of the tag with the mouse (by clicking the up/down arrow) or by type the value in the text field. Min/max and step values can be constant or dynamic expressions; the format specify the how the tag value will be displayed, see DecimalFormat class documentation
 for more information about the format. (secureable animation)
for more information about the format. (secureable animation)
Output
- Number make the graphic objects to display the numeric value provided by the code. The format of the displayed numeric value is the static text of graphic objects.
- String displays the string value of the tag/expression provided by the code. This animation has the ability to display the value of a numeric tag as a localized string using the tag properties.
- Localized displays a localized static text. The default version of the text is the static text of the graphic objects, you can add localized versions of the text for every language you want (select the language in main/all language lists and click the Add button the add the proper language code
 (lower-case, two-letter codes as defined by
(lower-case, two-letter codes as defined by  ISO 639 standard). Enter the localized version of the text at the right of the '=' simbol.
ISO 639 standard). Enter the localized version of the text at the right of the '=' simbol.
- Progress bar animation display a progress status in a progress bar object. Min/max values can be constant or dynamic expressions.
- Tabbed pane enable to display multiple windows in a multi tab frame. Optionally a tag can be linked to the index of the active tab (to receive/control the active tab).
- Image: the JavaCode provides a dinamic java.awt.Image
 object to be displayed in a image/button object.
object to be displayed in a image/button object.
- URL to set/get the
 URL of a HTML area object.
URL of a HTML area object.
Special
- Point location: the JavaCode returns a Point2D
 array with the dynamic Multipoint object point coordinates.
array with the dynamic Multipoint object point coordinates.
- Java Shape animation define which is the Shape
 of a Java Shape object. This animation/object couple is a way to use the generic Java Shape
of a Java Shape object. This animation/object couple is a way to use the generic Java Shape  interface to draw an object which has other standard object attributes (line/fill color, stroke and related animations).
interface to draw an object which has other standard object attributes (line/fill color, stroke and related animations).
- Java paint animation defines the way a Java Paint object is painted. The animation JavaCode receives the parameter a java.awt.Graphics2D
 object where to paint. For an example of this object/animation couple see the standard JSup Trend window: the time axis ticks and labels are painted in this way.
object where to paint. For an example of this object/animation couple see the standard JSup Trend window: the time axis ticks and labels are painted in this way.
Border/fill color
These animation define the line color of the object or its fill color.
- Binary color define a boolean value and two paints: one that will be used when the expression is false, and one when it's true.
- Thresholds color define numeric tag/expression whose value will be compared with a value/paint table to find which is the paint to be used. See Thresholds color animations for more details.
- Java Paint: the JavaCode provides a generic Java object that implements the standard java.awt.Paint
 interface to be used to paint the object.
interface to be used to paint the object.
- Bargraph (fill only): the value of the bargraph expression is used to draw the bargraph
 with various parameter/color/options that can be used in the Bargraph animation dialog. Read the tooltips in dialog for more detailed information.
with various parameter/color/options that can be used in the Bargraph animation dialog. Read the tooltips in dialog for more detailed information.
- Trend (fill only): this animation enable an object to display historical trends. Many tag / expression can be given to set/get various parameters.
Move/Size
Movement:
- Horizontal a smoothable animation that can move the object horizontally for the given number of pixel (left and right) in proportion to the expression value (between left/right value range).
- Vertical a smoothable animation that can move the object vertically for the given number of pixel (up and down) in proportion to the expression value (between up/down value range).
Resize:
- Horizontal a smoothable animation that can reduce the width of the object in proportion to the expression value (between min/max value range). The width cannot be increased with this animation, use an Affine transform animation to increase it.
- Vertical a smoothable animation that can reduce the height of the object in proportion to the expression value (between min/max value range). The height cannot be increased with this animation, use an Affine transform animation to increase it.
Special:
- Affine transformation: a very advanced animation where the JavaCode provides a java.awt.geom.AffineTransform
 object that will performs a linear mapping from 2D coordinates to other 2D coordinates of the object that preserves the "straightness" and "parallelness" of lines. Affine transformations can be constructed using sequences of translations, scales, flips, rotations, and shears. (smoothable)
object that will performs a linear mapping from 2D coordinates to other 2D coordinates of the object that preserves the "straightness" and "parallelness" of lines. Affine transformations can be constructed using sequences of translations, scales, flips, rotations, and shears. (smoothable)


