Tag classes are a useful way to define the properties of JSup tags.
Tag classes are organized in a hierarchical tree structure where a class inherits, adds and overrides the properties of its ancestors.
Why tag classes
Even if you have not to assign particular properties to a tag, it is a good practice to assign every tag to a tag class:
- It's a way to categorize tags and to explain their meaning / usage.
- If you later have to assign properties to a category of tags it will be a matter of seconds.
- It's a way put tags in groups that JavaCode can access at runtime. For example to create tasks for the JSup scheduler.
Class properties
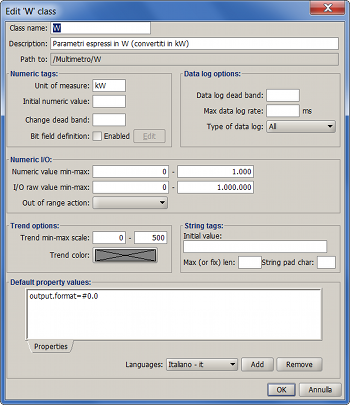
- Name: Must be as descriptive as possible because this will be the only info displayed in Tag Dialog (to see the parentage the tree combo button must be opened). The name must be unique within the parent class.
- Description: Only for later reference.
- Path to: a read only property that can be copied to be used in JavaCode to access the tag class (getTagClass( String path ) static method.
- Numeric tags properties - These properties will affect numeric tags only:
- Unite of measure: specify the default UM of the tags (see JSup UM support).
- Initial numeric value: Enter the value the tag will assume when the application starts and no retentive value is available.
- Change dead band: since tag processing is driven by change events, you can limit the minimum tag value variation that will be considered a change. For changes lesser than the given dead band no elaboration will be performed (no screen update, no code calculation, no alarm status update, etc).
- Bit field: see JSup tag bit fields.
- Value min-max: you can limit the range the belonging tags value can assume. If a value greater than the given maximum value is written to the tag, then the tag value will be the maximum; If a value lesser than the given minimum value is written to the tag, then the tag value will be the minimum.
- I/O raw value min-max: the range of the value read from and writter to remote I/O device (via I/O hook). These values (with Value min-max or the defaults if none) cause a tag value scaling on read/writes. If raw min-max are not specified or are the same of tag value min-max (or type default if none), then the tag is not scaled on read/write.
- Out of range action: the behavior when out of raw range values are read, if not specified the behavior for parent class will be used, otherwise:
- Force in range: if the raw value is less than the raw min, the raw min is considered instead of the read value.
- Ignore value: the value out of range is discarded and the tag value is not changed.
- Read error: the value out of range is discarded and the tag value is not changed and the channel read is considered not successful (End read tag, if any, is set to false).
- Trend options:
- Data logging options:
- Data log dead band: as the Change dead band, but to limit the data logging. Only changes lesser than the Data log dead band will not be considered to write a new record for the tag.
- Max data log rate: a different way to limit the frequency tag values will be written. If you enter a value (in milliseconds) than no more than a record every given ms will be written for a tag belonging to the class.
- Type of data log: When you limit the log rate (with the previous parameter), you can chose what kind of summary will be written for the tag:
- Max: only the maximum value from the previous record will be written.
- Min: only the minimum value from the previous record will be written.
- Mean: the mean value from the previous record will be written.
- All: Min/Mean/Max value from the previous record will be all written.
- String tags properties:
- Initial numeric value: Enter the value the tag will assume when the application starts and no retentive value is available.
- Max (or fix) length: the meaning depends of the type of the tags:
- String: it will be the maximum length of such tags.
- FLString: it will be the fixed length of such tags.
- Default property values: enter the values (even localized) for the default properties for tags belonging to this class (see Using tag properties).
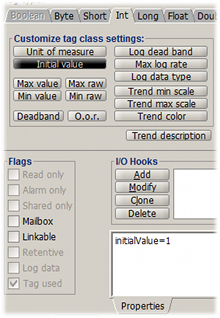
Custom tag properties
Many tag class properties can be specified directly by a tag using its own properties in the Tag Dialog.
Use the buttons of the Custumize tag class settings to define custom tag class properties for the tag.
The fact that a Tag Class property is customized within the tag properties is shown by the corresponding button (see the Initial value button on the right).


